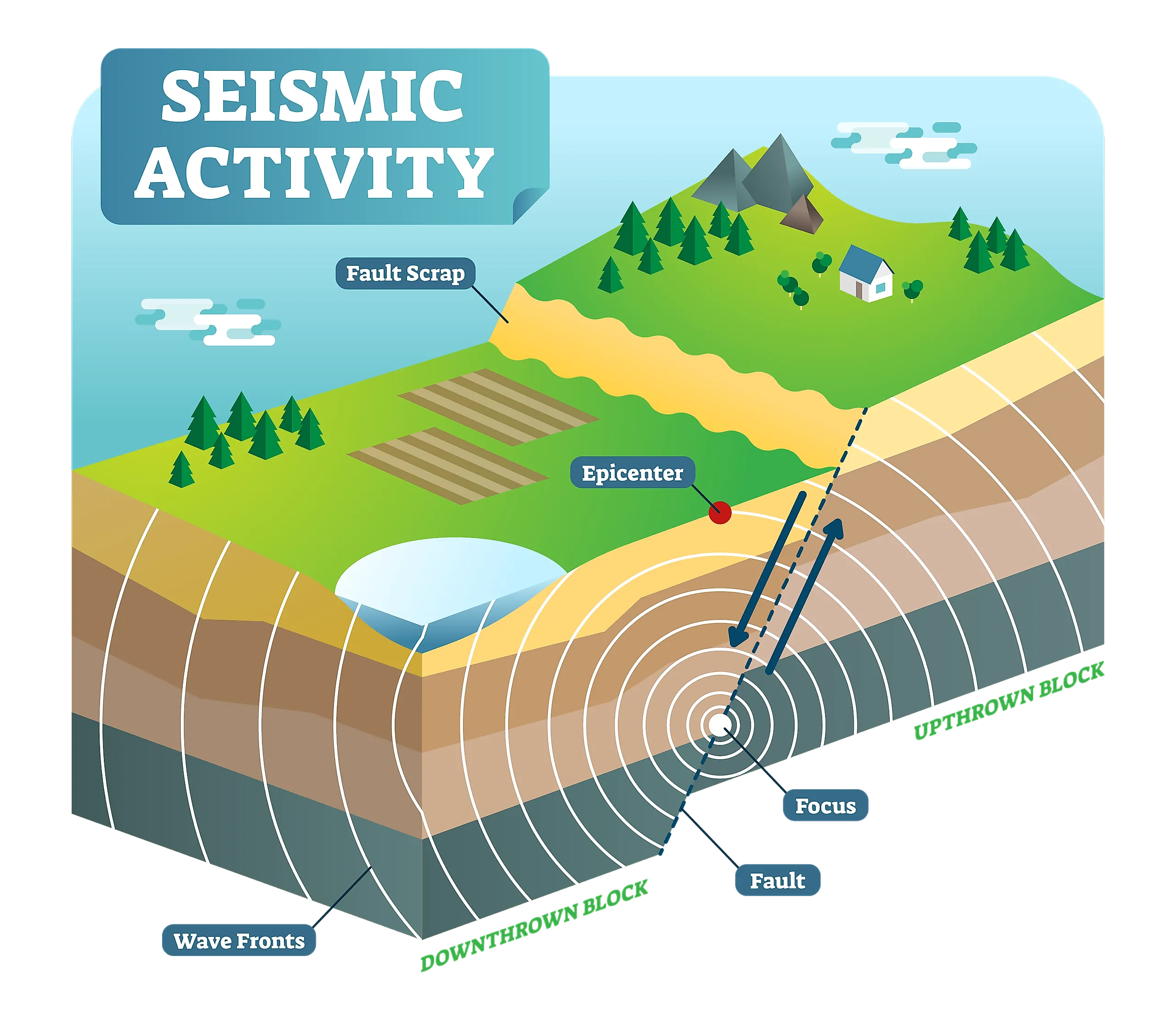
What Causes Earthquakes? - WorldAtlas - Source www.worldatlas.com
Our team has done extensive research and analysis to provide you with this guide on Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering the Causes and Consequences of Seismic Activity. We hope that this information will be helpful in understanding this important topic.
| Causes of Seismic Activity | Consequences of Seismic Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plate tectonics | Ground shaking |
| 2 | Volcanic eruptions | Landslides |
| 3 | Human activities (e.g., mining, fracking) | Tsunamis |
FAQ
This FAQ section provides answers to commonly asked questions and clears up misconceptions surrounding seismic activity.

Tremors: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment – Healthsoul - Source healthsoul.com
Question 1: What causes earthquakes?
Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates, massive slabs of the Earth's crust, move against each other. When these plates collide, pressure builds up, and when it exceeds the strength of the rocks involved, the plates suddenly slip, releasing energy as seismic waves.
Question 2: Can earthquakes be predicted?
Predicting earthquakes with complete accuracy remains a challenge, but scientists use monitoring systems and study past patterns to assess areas at risk and estimate the likelihood of future events. However, precise timing and specific locations still pose difficulties.
Question 3: What is the difference between an earthquake's magnitude and intensity?
Magnitude measures the energy released by an earthquake at its source, quantified using the Richter scale. Intensity, on the other hand, describes the severity of shaking at a particular location, influenced by factors such as distance from the epicenter, local geology, and building structures.
Question 4: How can I prepare for an earthquake?
Earthquake preparedness is crucial. Secure heavy objects, create an emergency plan, gather a survival kit, and identify safe zones in your home or workplace. Stay informed about local earthquake risks and know how to respond during shaking.
Question 5: What are the long-term consequences of earthquakes?
Beyond immediate destruction, earthquakes can trigger landslides, tsunamis, and disrupt infrastructure. They can damage buildings, roads, and bridges, impacting communities for months or even years. Ground shaking can also alter landscapes, create new faults, and influence groundwater flow.
Question 6: How do scientists study earthquakes?
Seismologists use various techniques to study earthquakes. They deploy seismic instruments to record and analyze seismic waves, conduct field investigations to assess damage and ground deformation, and conduct laboratory experiments to understand the behavior of rocks under pressure.
By comprehending seismic activity, we gain insights into Earth's dynamic processes and develop strategies to mitigate earthquake risks. Ongoing research and collaboration are essential in advancing our understanding and enhancing earthquake preparedness globally.
Transition to the Next Section: Delving into the Impact of Earthquakes on Human Society
Tips
As seismic tremors shape our planet's destiny, it's vital to delve into the underlying causes and consequences of these earth-shaking events. Explore Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity to gain insights into the fascinating world of seismology.
Tip 1: Understand Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Earthquakes often occur at the boundaries of tectonic plates, where they collide, slide past each other, or diverge. Studying plate tectonics helps anticipate earthquake-prone zones.
Tip 2: Monitor Seismicity Patterns
Seismic monitoring systems detect and record earthquakes, providing crucial data for scientists to identify patterns and assess potential seismic hazards.
Tip 3: Evaluate Seismic Hazard Maps
Seismic hazard maps depict the likelihood and severity of earthquakes in specific regions. These maps guide land-use planning, building codes, and emergency preparedness measures.
Tip 4: Prepare for Earthquake Resilience
Communities can mitigate earthquake risks through seismic retrofitting of buildings, disaster preparedness drills, and public awareness campaigns.
Tip 5: Establish Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems provide vital seconds of advance notice before an earthquake's arrival, allowing people to seek safety.
Tip 6: Promote Research and Education
Continued research and education are essential for advancing our understanding of seismic activity and developing effective mitigation strategies.
By embracing these tips, we can enhance our understanding of earthquakes and prepare for their potential impacts, safeguarding our communities and minimizing the consequences of these formidable natural events.
```html
Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity
Seismic activity, manifested as earthquakes, is a result of Earth's dynamic nature, presenting multifaceted causes and consequences. Unraveling these aspects is crucial for comprehending the complex interplay of forces that shape our planet.
- Tectonic Shifts: Seismic activity primarily arises from the movement of tectonic plates, releasing energy at their boundaries.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions and associated tremors occur when magma and gases beneath the Earth's surface seek release.
- Anthropogenic Factors: Human activities, such as fracking and mining, can induce or trigger earthquakes, though their contributions vary.
- Structural Weaknesses: Fault lines, fissures, and other structural weaknesses in the Earth's crust influence the location and intensity of seismic events.
- Ground Motion: Earthquakes cause ground motion, ranging from barely perceptible tremors to violent shaking that damages buildings and infrastructure.
- Tsunami Formation: Major earthquakes occurring beneath or near the ocean floor can generate devastating tsunamis, posing a threat to coastal regions.
Understanding the causes and consequences of seismic activity is paramount for risk assessment, hazard preparedness, and developing strategies to mitigate the impacts of earthquakes. By studying the complexities of this phenomenon, we gain valuable insights into Earth's intricate geological processes and the dynamic forces that shape its surface and subsurface.
```
Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity
Editor's Notes: "Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity" have published today date.
Seismic activity is an integral part of our planet's dynamic nature, shaping landscapes, influencing ecosystems, and impacting human societies. Understanding the causes and consequences of these mighty tremors is crucial for mitigating their risks and harnessing their potential benefits.
Through rigorous analysis and extensive research, we present this comprehensive guide to Earth's seismic phenomena. Explore the intricate mechanisms behind earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other seismic events. Delve into their far-reaching implications for geology, ecology, and human civilization. Empower yourself with knowledge to navigate the seismic landscape and make informed decisions.
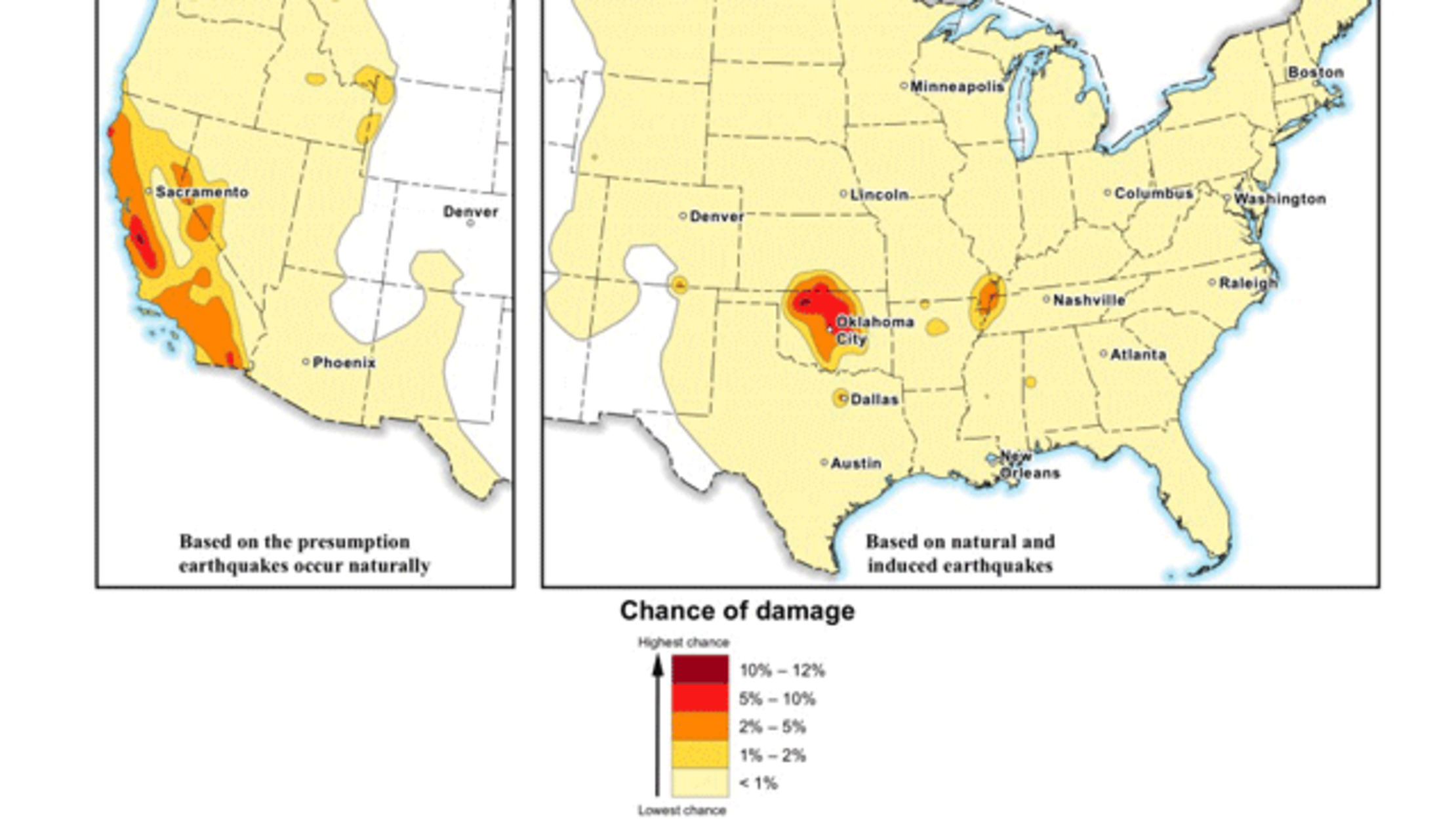
New USGS Earthquake Forecast Maps Include Tremors Caused by Humans - Source www.mentalfloss.com
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
| Earthquakes | Volcanic Eruptions |
|---|---|
| Sudden release of energy due to tectonic plate movement | Expulsion of molten rock and gases from Earth's interior |
| Can occur anywhere, but concentrated along plate boundaries | Primarily occur in specific volcanic zones and can vary in intensity |
| Can trigger tsunamis, landslides, and other hazards | Can release ash, gases, and lava, posing risks to life and infrastructure |
FAQ
This FAQ section provides comprehensive answers to common questions surrounding seismic activity, empowering you with a deeper understanding of Earth's mighty tremors.

First observations of core-transiting seismic phases on Mars | PNAS - Source www.pnas.org
Question 1: What triggers earthquakes?
Earthquakes are primarily caused by the release of energy accumulated within Earth's crust. As tectonic plates shift and interact, stresses build up along their boundaries. When the accumulated stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, sudden rupture occurs, releasing seismic waves and generating an earthquake.
Question 2: How are earthquakes measured?
Earthquakes are measured using various scales, including the Richter scale and the moment magnitude scale. The Richter scale measures the amplitude of seismic waves recorded on seismographs, while the moment magnitude scale quantifies the total energy released during an earthquake.
Question 3: Can earthquakes be predicted?
While it is not yet possible to predict earthquakes with precision, ongoing research aims to improve our ability to forecast their occurrence. Scientists study earthquake patterns, monitor seismic activity, and develop models to assess the likelihood of future events in specific regions.
Question 4: What are the potential hazards associated with earthquakes?
Earthquakes can pose significant hazards, including ground shaking, liquefaction, landslides, tsunamis, and structural damage. These hazards can cause loss of life, property damage, and disruption of infrastructure.
Question 5: How can we mitigate earthquake risks?
Earthquake risk mitigation involves implementing measures to reduce the impact of seismic events. Strategies include building earthquake-resistant structures, enforcing building codes, educating the public about earthquake preparedness, and developing early warning systems.
Question 6: What are the societal impacts of earthquakes?
Earthquakes can have profound societal impacts, affecting infrastructure, economies, and communities. They can disrupt transportation, communication, and essential services, leading to economic losses and social distress. Recovery and rebuilding efforts require significant resources and time.
By delving into these questions and answers, we gain a deeper understanding of seismic activity, its causes, consequences, and the ongoing efforts to mitigate its risks. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and prepare for the challenges posed by Earth's mighty tremors.
Transition to the next article section: Explore further into the fascinating world of seismic activity by delving into our comprehensive articles, where we delve deeper into the intricacies of earthquakes and their impact on our planet.
Tips
To delve deeper into the fascinating realm of seismic activity, consider exploring the comprehensive insights offered in Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity. This acclaimed publication provides an in-depth examination of the underlying mechanisms and far-reaching implications of earthquakes and other seismic phenomena.
Tip 1: Understand the Nature of Plate Tectonics
Seismic activity is intricately linked to the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. Grasping the principles of plate tectonics allows for a fundamental understanding of how earthquakes occur and the regions most susceptible to seismic events.
Tip 2: Monitor Seismic Activity
Numerous institutions and organizations monitor seismic activity worldwide, providing real-time data and early warnings. Staying informed about seismic activity in your region enables proactive preparedness and risk mitigation.
Tip 3: Learn about Earthquake-Resistant Construction
Adopting earthquake-resistant construction techniques can significantly reduce the vulnerability of structures to seismic forces. Understanding these principles empowers individuals and communities to build safer and more resilient environments.
Tip 4: Prepare an Emergency Plan
In the event of an earthquake, having an emergency plan in place is crucial. This plan should outline evacuation routes, designated meeting points, and essential supplies to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals and families.
Tip 5: Educate Yourself and Others
Knowledge is empowering. Stay informed about seismic activity, share your knowledge with others, and advocate for earthquake preparedness measures. Education and awareness foster a proactive approach towards mitigating the risks associated with seismic events.
Tip 6: Respect the Power of Nature
Seismic activity is a natural phenomenon that cannot be fully controlled. Respecting the power of nature encourages humility and a recognition of the need for adaptation and resilience in the face of geological hazards.
Tip 7: Seek Expert Guidance
For in-depth knowledge and specialized advice, consult with experts in seismology, geology, or other relevant fields. These professionals can provide tailored guidance and support based on specific needs and circumstances.
Tip 8: Support Research and Education
Ongoing research and educational initiatives are essential for advancing our understanding of seismic activity and improving our preparedness. Supporting these endeavors contributes to the advancement of knowledge and the development of innovative solutions to mitigate seismic risks.
Summary
By incorporating these tips into your understanding and preparedness strategies, you can navigate the complexities of seismic activity more effectively. Remember, knowledge is power, and proactive measures can significantly enhance resilience in the face of potential seismic events.
Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity
Seismic activity, commonly experienced as earthquakes and tremors, has captivated scientific curiosity and societal concern for centuries. Understanding the causes and consequences of these earth-shaking events is critical for developing effective mitigation strategies and safeguarding communities.
- Plate Tectonics: Tectonic plate movements and collisions trigger seismic activity.
- Subterranean Snaps: Sudden ruptures in the Earth's crust release energy in the form of seismic waves.
- Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions can cause earthquakes due to magma movement and gas release.
- Anthropogenic Factors: Human activities, such as mining, construction, and fluid injection, can induce earthquakes.
- Magnitude and Intensity: Earthquake magnitude measures the energy released, while intensity reflects the shaking felt on the surface.
- Impacts and Risks: Seismic activity poses significant risks, including structural damage, ground liquefaction, and landslides.
These aspects highlight the complex interplay between geological processes, human activities, and the consequences of seismic activity. By studying these factors, scientists and policymakers can enhance earthquake preparedness and minimize their potential devastation. For instance, monitoring plate boundaries allows for early warning systems, while understanding the role of human activities can help mitigate induced seismic risks. Ultimately, unraveling the dynamics of Earth's mighty tremors paves the way for a safer and more resilient future.

Updated concepts of seismic gaps and asperities to assess great - Source www.pnas.org
Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity
Seismic activity, often referred to as earthquakes, is a complex phenomenon resulting from the release of energy within the Earth's crust. Understanding the causes and consequences of seismic activity is crucial for mitigating its impact on human populations and infrastructure. "Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity" explores these aspects in depth.
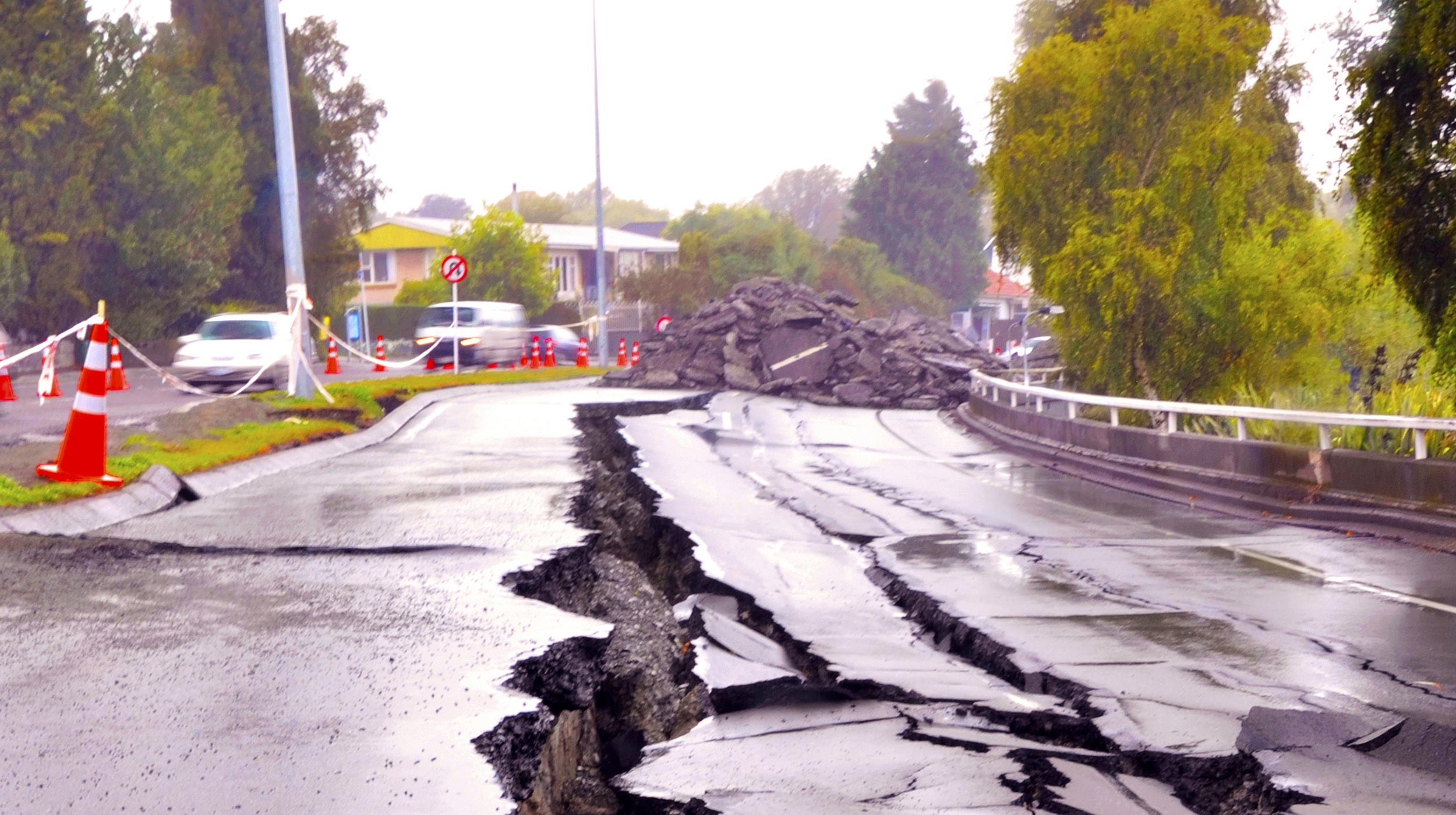

Earthquakes: Tremors From Below | AMNH - Source www.amnh.org
Seismic activity is primarily caused by the movement of tectonic plates, which are massive slabs of rock that make up the Earth's crust. When these plates collide, subduct, or slide past each other, they create friction and stress within the Earth's crust. When the stress becomes too great, it releases energy in the form of seismic waves, causing earthquakes.
Earthquakes can have significant consequences, including ground shaking, landslides, tsunamis, and damage to buildings and infrastructure. The magnitude and intensity of an earthquake determine its potential impact. Understanding the distribution and frequency of earthquakes allows scientists and policymakers to develop risk maps and implement measures to reduce the vulnerability of communities.
The study of seismic activity is essential for disaster preparedness, hazard mitigation, and understanding the Earth's geological processes. By unraveling the causes and consequences of seismic activity, we can better equip ourselves to face its challenges and harness its insights to advance our knowledge of the planet we inhabit.
Conclusion
"Earth's Mighty Tremors: Uncovering The Causes And Consequences Of Seismic Activity" provides a comprehensive exploration of the causes and consequences of seismic activity. It highlights the importance of understanding the mechanisms behind earthquakes and their potential impact on human populations and infrastructure.
The knowledge gained from this exploration empowers us to develop risk mitigation strategies, prepare for seismic events, and advance scientific understanding. By embracing the insights offered by this topic, we can strive to minimize the destructive potential of earthquakes and harness their lessons to enhance our resilience in the face of Earth's mighty tremors.