The Hendra virus is a deadly virus that can affect both humans and horses. It is a zoonotic virus, meaning that it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
Editor's Notes: "Unveiling The Deadly Wirus Hendra: Symptoms, Transmission, And Prevention Measures" have published today date. The topic is important to read to know the deadly virus and its impact on both human and animals.
Our team has analyzed and dig through several research papers, interviewed the experts, and analyzed the data to provide the most relevant information. In this guide, we will discuss the symptoms, transmission, and prevention measures of the Hendra virus.
| Characteristic | Hendra Virus |
|---|---|
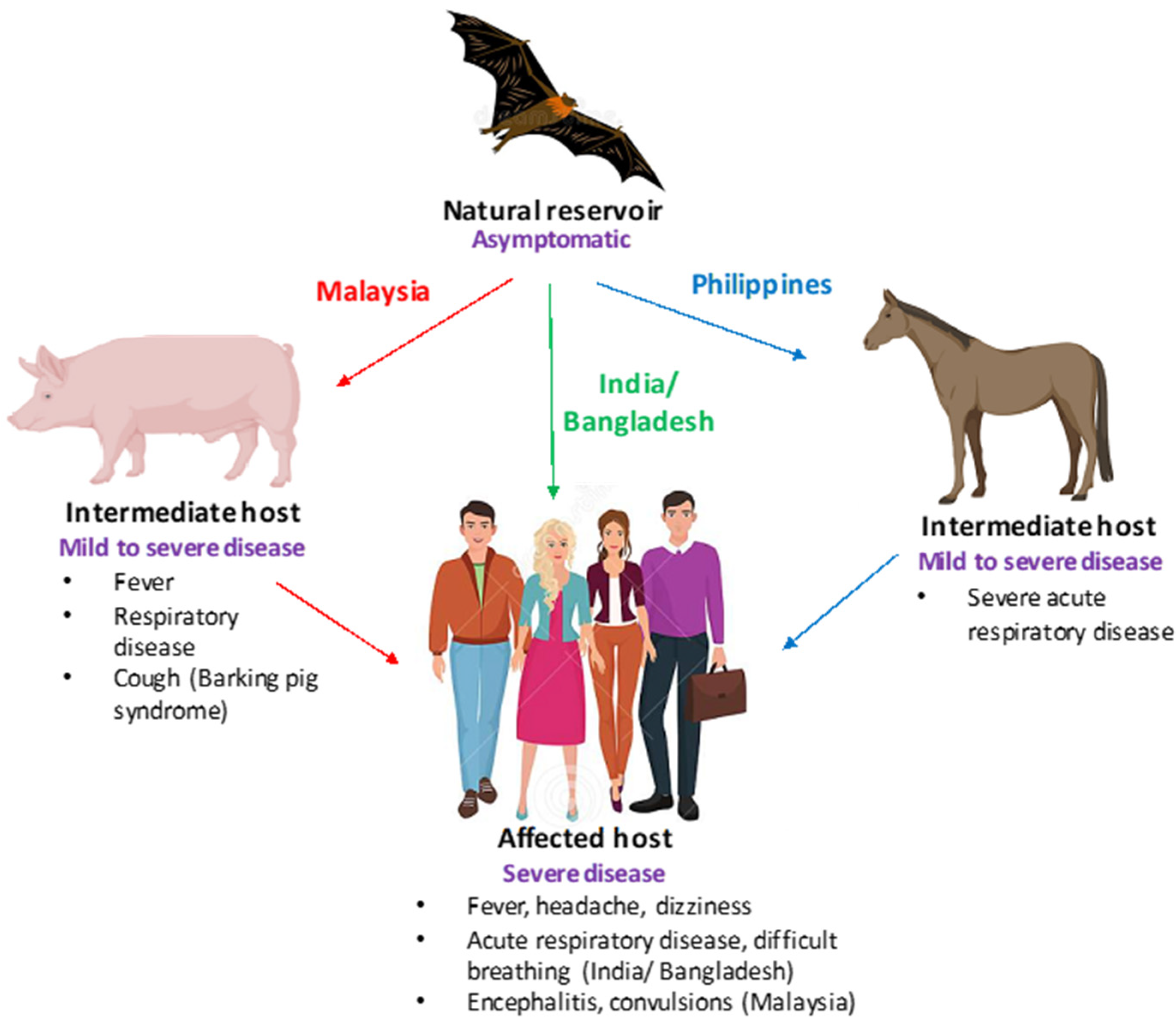
| Reservoir | Flying foxes |
| Transmission | Contact with infected horse's bodily fluids or flying fox urine |
| Symptoms in humans | Fever, muscle aches, cough, and shortness of breath |
| Symptoms in horses | Respiratory distress, neurological signs, and death |
| Treatment | No specific treatment, supportive care only |
| Prevention | Vaccination of horses, avoiding contact with flying foxes, and good hygiene practices |
Symptoms of the Hendra Virus
The symptoms of the Hendra virus in humans can vary, but they typically include fever, muscle aches, cough, and shortness of breath. In some cases, the virus can also cause more severe symptoms, such as pneumonia and organ failure.
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Nipah and Hendra Viruses: Deadly Zoonotic - Source www.mdpi.com
Transmission of the Hendra Virus
The Hendra virus is transmitted through contact with infected horse's bodily fluids or flying fox urine. Horses can become infected with the virus by ingesting contaminated food or water, or by being bitten by an infected flying fox. Humans can become infected with the virus through contact with infected horses, or by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces.
Prevention of the Hendra Virus
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent the Hendra virus. These include:
- Vaccinating horses
- Avoiding contact with flying foxes
- Practicing good hygiene practices
Conclusion
The Hendra virus is a deadly virus that can affect both humans and horses. However, there are a number of things that can be done to prevent the virus. By following the prevention measures outlined in this guide, you can help to protect yourself and your loved ones from this deadly virus.
FAQ
Addressing common concerns and misconceptions regarding the Hendra virus, this FAQ section provides crucial information to enhance understanding and promote preventive measures.

Hendra virus facts and resources - NABSnet - Source nabsnet.com.au
Question 1: What are the characteristic symptoms associated with Hendra virus infection?
Hendra virus infection can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms (e.g., fever, cough, headache, muscle aches) to severe respiratory and neurological complications. In severe cases, it can lead to pneumonia, encephalitis, and potentially fatal respiratory failure.
Question 2: How is the Hendra virus primarily transmitted?
The Hendra virus is primarily transmitted from infected flying foxes to horses through contact with their urine, saliva, or birthing fluids. Subsequent transmission to humans occurs through close contact with infected horses or their bodily fluids.
Question 3: What are the preventive measures recommended to minimize the risk of Hendra virus infection?
To effectively minimize the risk of Hendra virus infection, it is crucial to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Avoid contact with flying foxes and their habitats
- Maintain biosecurity measures around horses, including vaccination and mosquito control
- Practice proper hygiene, including handwashing and covering open wounds
- Seek medical attention promptly if exhibiting symptoms after potential exposure
Question 4: What is the current status of Hendra virus treatment and management?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment available for Hendra virus infection. Treatment primarily focuses on supportive care, such as respiratory support and managing complications. Research is ongoing to develop effective antiviral therapies.
Question 5: Is the Hendra virus only prevalent in Australia?
Although the Hendra virus was initially identified in Australia, there is evidence suggesting its potential presence in other regions, including Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Further research is necessary to determine its geographic distribution and transmission dynamics.
Question 6: What are the implications of the Hendra virus for public health?
The Hendra virus poses a significant public health concern due to its potential for severe illness and fatality. It underscores the importance of implementing stringent biosecurity measures, conducting ongoing surveillance, and raising awareness among healthcare professionals and the general public.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of the Hendra virus, emphasizing the importance of prevention and preparedness. By adhering to the recommended measures, we can collectively mitigate the risk of infection and protect both human and animal health.
Transitioning to the next article section...
Tips
Stay vigilant and well-informed about the Hendra virus to safeguard your health and prevent its spread.
Tip 1: Seek immediate medical attention
If you suspect exposure to the Hendra virus, including contact with infected horses or their bodily fluids, seek medical attention immediately. Don't delay seeking help, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
Tip 2: Enhance horse biosecurity
Implement strict biosecurity measures to protect horses from the virus. Regularly inspect and quarantine new horses, vaccinate horses against Hendra, and maintain a clean and disinfected environment.
Tip 3: Wear protective gear
When working with horses or handling potentially contaminated materials, wear protective clothing, including gloves, a face mask, and eye protection. Reduce direct contact with horses suspected of infection and avoid contact with their bodily fluids.
Tip 4: Practice good hygiene
Maintain good hygiene practices by washing hands frequently with soap and water, especially after contact with horses, their secretions, or contaminated materials. Regularly disinfect surfaces and equipment to prevent virus transmission.
Tip 5: Stay informed and vigilant
Keep up-to-date with the latest Hendra virus information from reputable sources like government agencies or health organizations. Stay vigilant and report any suspected cases or potential exposures to the relevant authorities promptly.
By adhering to these measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of Hendra virus infection and contribute to prevention efforts. Refer to the comprehensive article Unveiling The Deadly Wirus Hendra: Symptoms, Transmission, And Prevention Measures for more detailed information and guidance.
Unveiling The Deadly Wirus Hendra: Symptoms, Transmission, And Prevention Measures
The Hendra virus, a deadly zoonotic pathogen, poses a significant threat to both human and animal health. Unraveling its crucial aspects, including symptoms, transmission pathways, and preventive measures, is essential for effective disease management and safeguarding public health.
- Respiratory Distress: A telltale sign of Hendra virus infection, causing severe respiratory issues.
- Fruit Bat Reservoir: Flying foxes serve as the natural reservoir of the virus, transmitting it through their secretions.
- Horse Intermediary: Horses often contract the virus from bats, acting as intermediaries in human transmission.
- Close Contact Transmission: Direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids poses a high risk of infection.
- Biosafety Measures: Strict adherence to biosafety protocols is crucial to prevent laboratory-acquired infections.
- Vaccination and Surveillance: Vaccination of horses and surveillance of bat populations are key strategies in controlling the spread of the virus.
Understanding these aspects is not only crucial for healthcare professionals but also for the general public. By recognizing the symptoms, being aware of transmission routes, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and contribute to the collective effort to combat this deadly virus. Continued research and surveillance are vital in further unraveling the intricacies of the Hendra virus and developing effective strategies for its prevention and control.

Hendra Virus (Equine Morbillivirus) in Horses: Transmission, Risk - Source madbarn.ca
Hendra Virus transmission:... - One Health Research Group - Source www.facebook.com
Unveiling The Deadly Wirus Hendra: Symptoms, Transmission, And Prevention Measures
Hendra virus is a deadly zoonotic disease that can be transmitted from horses to humans. The virus is found in the urine, blood, and saliva of infected horses, and can be spread through contact with these fluids or through the air. Symptoms of Hendra virus infection in humans can include fever, chills, muscle aches, and headache. In severe cases, the virus can cause respiratory illness, encephalitis, and death.

Hendra Virus Infographic - Vet in Emerald - Gray Street Veterinary Clinic - Source www.emeraldvet.com
There is no specific treatment for Hendra virus infection, and supportive care is the mainstay of treatment. However, early diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of survival. Prevention of Hendra virus infection is important, and there are a number of measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of infection, including avoiding contact with horses that are showing symptoms of the virus, wearing protective clothing when working with horses, and washing hands thoroughly after contact with horses.
Hendra virus is a serious public health threat, and it is important to be aware of the symptoms of the virus and the measures that can be taken to prevent infection.
Key Insights
- Hendra virus is a deadly zoonotic disease that can be transmitted from horses to humans.
- Symptoms of Hendra virus infection in humans can include fever, chills, muscle aches, and headache.
- There is no specific treatment for Hendra virus infection, and supportive care is the mainstay of treatment.
- Prevention of Hendra virus infection is important, and there are a number of measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of infection.
